Cryptocurrency 101: Introduction to the Blockchain and Crypto Currency Mining

Written by: Catherine Buck, CFP®
Introduction:
We are all familiar with exchanging money using mobile payment services like PayPal, Zelle or Venmo. These money transferring services are managed by third parties that control every aspect of the transaction with the power to decline a transfer through transaction limits, charge a fee on the transaction, and store personal information pertaining to each transaction. Some people found the lack of security and control in money exchanges as inspiration to create cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies were established as an alternative to financial institutions and governments, creating a decentralized, secure, and transparent method of transferring and storing currency.
This blog will highlight cryptocurrencies using Bitcoin as its primary example, as it is the most popular cryptocurrency on the market. Briefly, Bitcoin was created in 2009 anonymously by Satoshi Nakamoto, it is unknown if this was an individual or group of people. Bitcoin was created in response to the 2008 financial crisis, as its creation date suggests. The creator(s) believed the centralized financial system was flawed and corrupt. Bitcoin, like many cryptocurrencies, has a fixed supply of 21 million Bitcoins or BTC making them “inflation resistant”. Per the Blockchain Council™ there are 1.5 million BTCs remaining to be mined and will be completely mined by the year 2140.
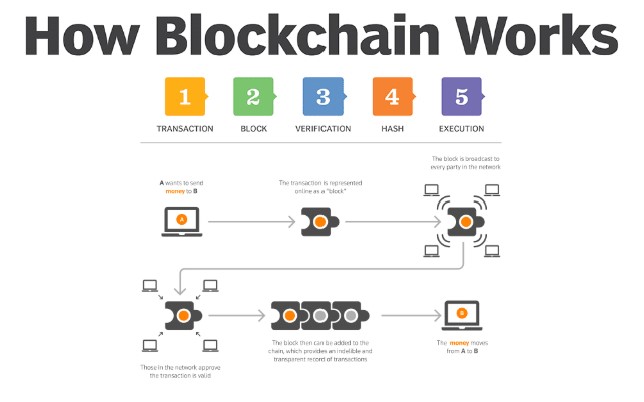
What is the Blockchain:
Let us begin with a singular transaction between two people, John and Sally. John pays Sally 1 BTC for a used car. I won’t go into the minutia of bitcoin transaction, but this transaction is known as a “block”. A block is an encrypted record or receipt containing transaction information and owner balances. Each party will have their own block pertaining to a transaction, every transaction may contain two or more validated blocks that create a blockchain. These transaction histories are ledgers that preserve and validate crypto currency exchange between parties. Keeping third party managers out and protecting currency exchange with strong encryption. Each cryptocurrency uses its own, unique encryption. Bitcoin uses a hashing algorithm called SHA256 to encode transaction data between users where it cannot be counterfeited or altered in any way. But a blockchain cannot truly be created until each block, or transaction, is validated.
Mining Bitcoin:
To create a blockchain, blocks must be validated prior to adding them to the blockchain. Essentially, validating the information within a single block or transaction and then linking those transactions together to complete the ledger of transaction information. Who validates the blocks? A cryptocurrency miner. The crypto miner must solve a complex mathematical problem to validate a single block to calculate the “specific has value of the block”. From there, the correct hash value will be reviewed and validated by other miners before it is added to the blockchain. Every block validated and added to the blockchain rewards the initial successful miner with cryptocurrency, in 2024 a miner is rewarded 3.125 BTC per block validation. Simply, miners are paid to validate blocks and add them to the blockchain, this is known as “mining”. Miners typically use a lot of computing power to calculate these complex mathematical problems, known as “Proof of work,” which can result in owning large quantities of computing hardware, specific mining software, and a large amount of electricity which can be expensive as crypto mining consumes significant power.
Where do Cryptocurrencies Fall into my Portfolio?
With Bitcoin surpassing $100,000 it has been the hot topic lately, even reaching $107,000 this past week. Cryptocurrencies are still very speculative investments and therefore aren’t necessarily added to a well-diversified, long-term investment strategy. If you feel inclined to add cryptocurrency to your portfolio, it should be a small percentage of your total portfolio’s value. If you have any further questions, please contact our office to be connected with a trusted financial advisor.
Bouchey Financial Group has offices in Saratoga Springs and Historic Downtown Troy, NY as well as Boston, MA and Jupiter, FL.